Payment and Transfer
General Banking Services
Notes and Coins
Banking Regulatory and Supervisory RegimeBanking Legislation, Policies and Standards ImplementationBanking Conduct and EnforcementAnti-Money Laundering and Counter-Financing of TerrorismResolution RegimeSmart BankingRegulatory GuidesRegtech Knowledge HubHKMA – BIS Joint ConferenceGreen and Sustainable Banking Conference
Hong Kong as an International Financial CentreFintechBond Market DevelopmentFinancial Market InfrastructureStored Value Facilities and Retail Payment SystemsStablecoin IssuersSoft InfrastructureInternational & Regional Financial Co-operationCentre for Green and Sustainable FinanceHKMA Infrastructure Financing Facilitation OfficeCross-boundary Wealth Management Connect Scheme in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay AreaGlobal Financial Leaders' Investment SummitHKMA – BIS High-Level ConferenceHong Kong Green Week – Finance Stream
Banking Regulatory and Supervisory RegimeBanking Legislation, Policies and Standards ImplementationBanking Conduct and EnforcementAnti-Money Laundering and Counter-Financing of TerrorismResolution RegimeSmart BankingRegulatory GuidesRegtech Knowledge HubHKMA – BIS Joint ConferenceGreen and Sustainable Banking Conference
Hong Kong as an International Financial CentreFintechBond Market DevelopmentFinancial Market InfrastructureStored Value Facilities and Retail Payment SystemsStablecoin IssuersSoft InfrastructureInternational & Regional Financial Co-operationCentre for Green and Sustainable FinanceHKMA Infrastructure Financing Facilitation OfficeCross-boundary Wealth Management Connect Scheme in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay AreaGlobal Financial Leaders' Investment SummitHKMA – BIS High-Level ConferenceHong Kong Green Week – Finance Stream



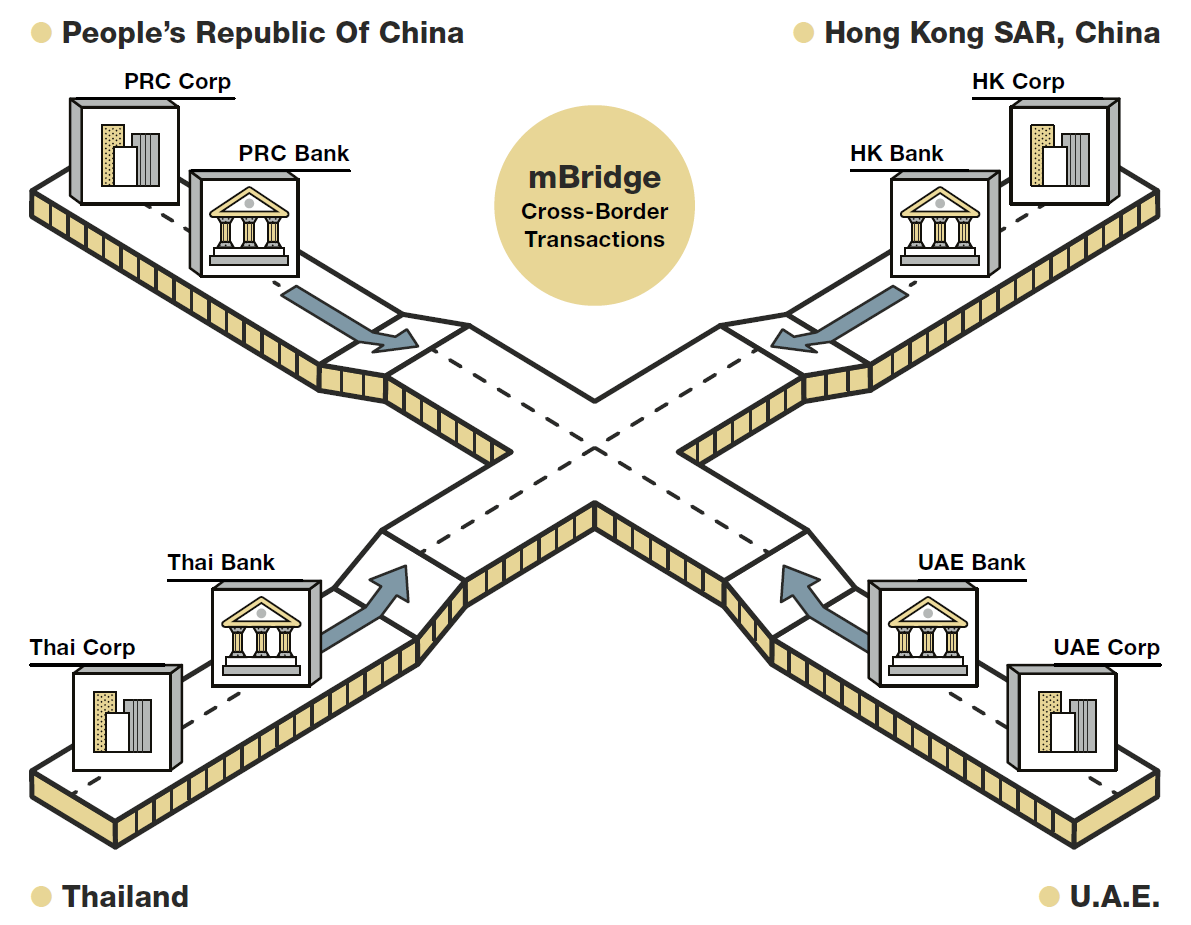





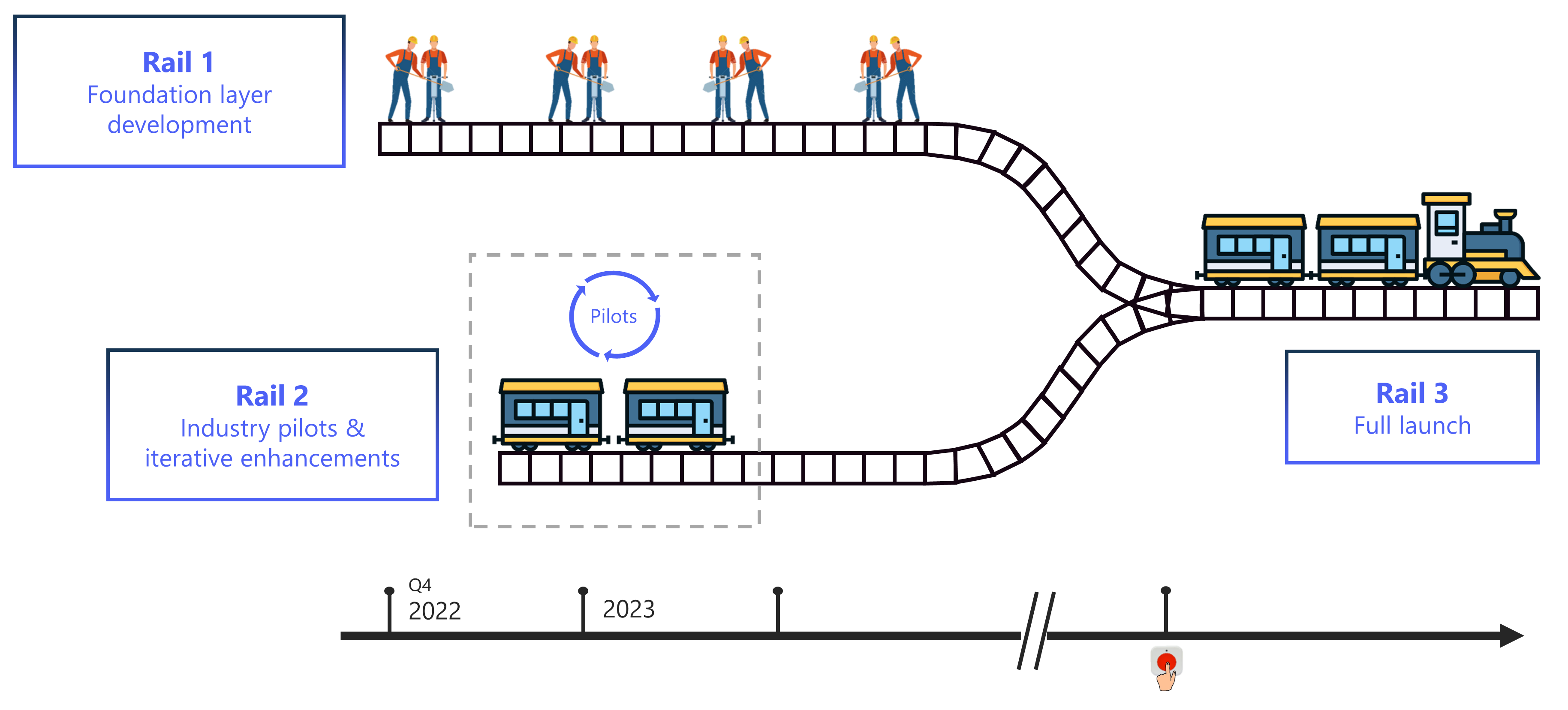
 .jpg)
